Discipline of Systems Biology
JapaneseTopics
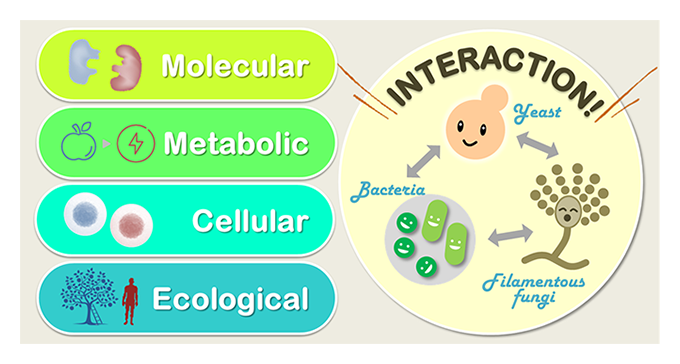
- Microbial ecology in traditional food fermentation
- Health-promoting effect of fermented food ascribed to Aspergillus oryzae
- TOR (Target of Rapamycin) signaling pathway
Topics
- Endoplasmic reticulum stress and unfolded protein response
- Industrially functional yeast strains carrying enforced organelles
- Approach to human diseases using yeast as a model organism
Topics
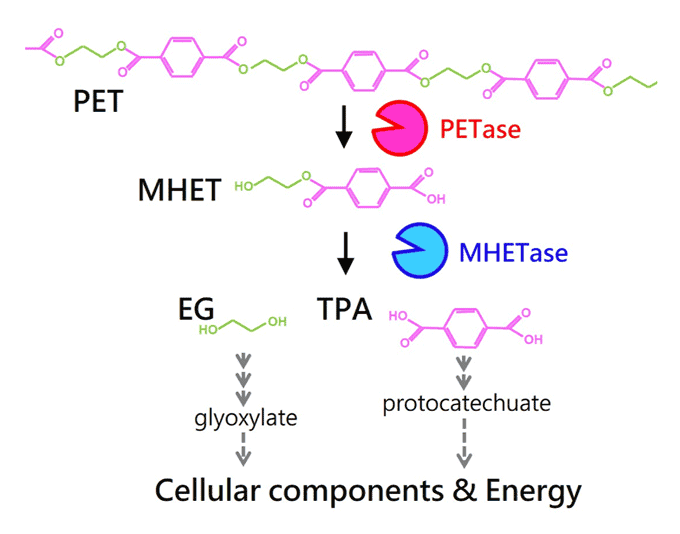
- Elucidation of a bacterial PET metabolism
- Fermentation of plastics
- Visualizing microbiology
Topics
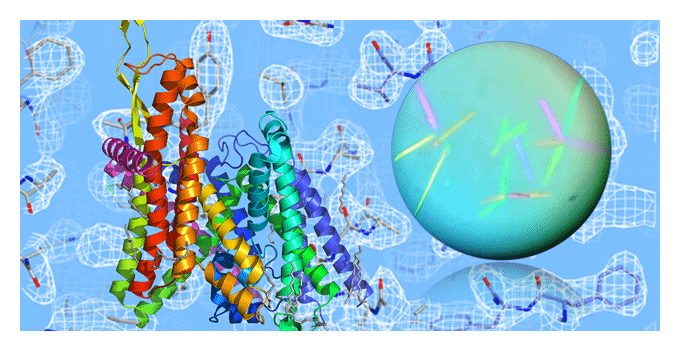
- Visualization of the Operational Mechanism of the Sec Membrane Protein Complex at the Atomic Level
- Unraveling the Intricate Mechanisms of Ion Transporters
- Cutting-Edge Analysis Using Advanced Technologies
Topics
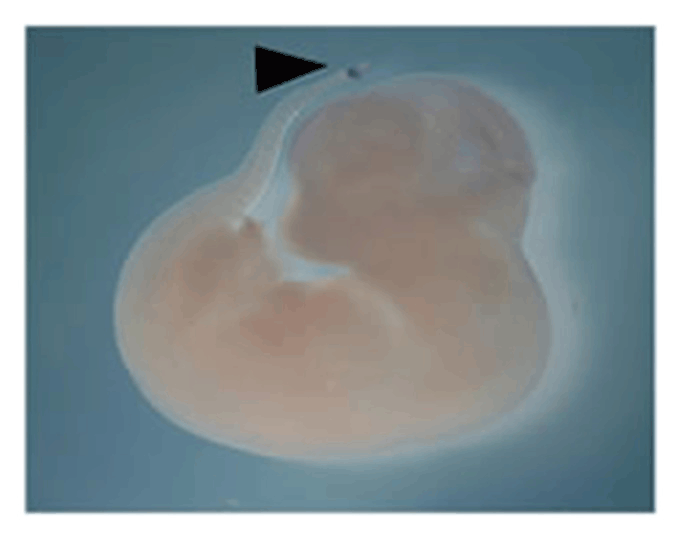
- Research for somitogenesis in vertebrates as a model system for the biological clock
Topics
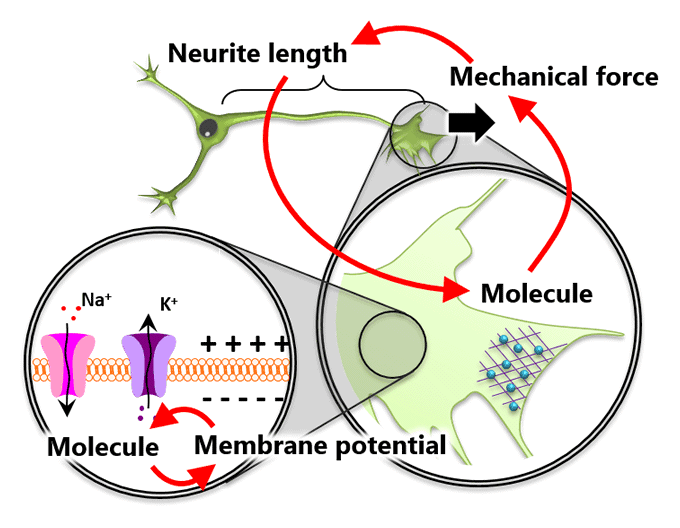
- Axon/dendrite formation and neuronal polarization
- Mechanical forces for axon guidance and cell migration
- Actin waves: a new mechanism for cellular protein transport
- Research in medicine: brain diseases and cancer metastasis
Topics
- Isolation and improvement of elements involved in high expression of transgene
- Elucidation of the mechanisms of phenotypic control and adaptive evolution by gene expressions
- Elucidation of the environmental adaptation mechanism of plants through gene expression
Topics
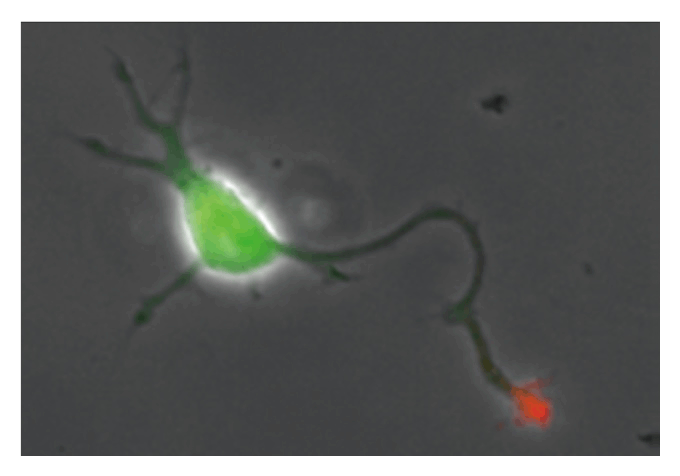
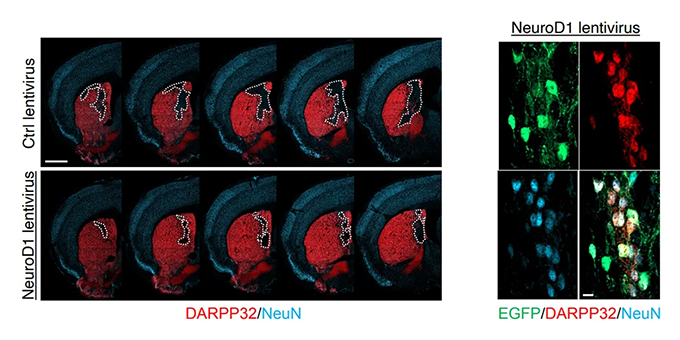
- Reprogramming Human Somatic Cells into Neurons
- Application to Neurological Disease Treatment
- Development and Application of Novel Cell Reprogramming Technologies
Topics
- Systems Biology of Cell Deformation and Migration (From molecules to cells)
- Systems Biology of Tissue Formation (From cells and tissues)
- Medical Systems Biology (From molecules and tissues to human diseases)
- Preprocessing and Machine Learning Applications for Biological Data Analysis