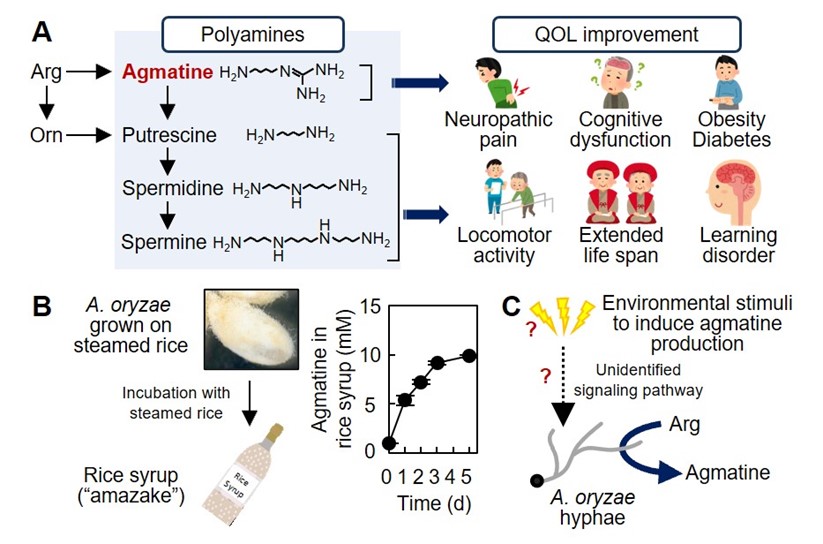
A variety of traditional fermented foods have been produced since ancient times in Japan, and have been contributing to Japanese healthy life span. However, why the fermented foods are beneficial for our health remains scientifically well understood. Our major aim is to clarify the health-promoting effects of fermented foods from the view point of microbiology. The filamentous fungus Aspergillus oryzae is a key microbe in the production of various fermented foods as it produces hydrolyzing enzymes to degrades raw materials such as grains and soy bean. Our recent studies have revealed that A. oryzae produces significant amount of agmatine, a natural polyamine that improves the quality of life (QOL), highlighting the significance of A. oryzae not only in the source of hydrolyzing enzymes but also in the enhancement of our health. We are investigating the molecular mechanisms of the physiologically active polyamine production by A. oryzae. The resultant findings are expected applicable for the development of novel fermented foods and nutraceuticals with increased functionalities to promote healthy life span in aging/aged society (see below).
【Related Papers】
- Murakami, S. Ikuta, W. Fukuda, N. Akasaka, J. Maruyama, S. Shinma, E. Fukusaki, and S. Fujiwara*; Identification and enzymatic properties of arginine decarboxylase from Aspergillus oryzae; Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 90(5): e0029424 (2024)
- N. Akasaka and S. Fujiwara*; The therapeutic and nutraceutical potential of agmatine, and its enhanced production using Aspergillus oryzae; Amino Acids 52(2): 181-197 (2020)
- N. Akasaka, S. Kato, S. Kato, R. Hidese, Y. Wagu, H. Sakoda, and S. Fujiwara; Agmatine production by Aspergillus oryzae is elevated by low pH during solid-state cultivation; Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 84(15): e00722-18 (2018)
